Doubly Linked List | C++ Implementation
The nodes in a linked list are connected through pointers. Pointers represent the address of a location in a memory. The order in a linked list is determined by a pointer in each node. A node in a doubly linked list contains a data item and a node pointer to the next node. In a singly linked list we can traverse only in one direction.
The first node of the linked list is the head and the last node is the tail. If head is NULL then the list is empty.
In C++, a node can be defined using struct, which contain a data item and a pointer to next node.
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
Node(T val): data(val), next(nullptr){}
};
Node(T val): data(val), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {} is the constructor for the struct Node which is used to initialise data, next and prev. T means it is a generic struct and data can store values of all data types.
To declare head: Node *head, *tail;
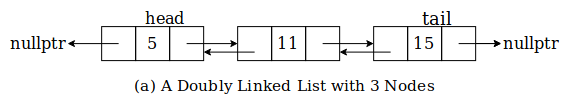
In the above fig. Node containing 5 is head and node containing 15 is tail.
The three basic operations supported by a linked list are searching, insertion and deletion.
The search function for doubly linked list is same as the search function for singly linked list.
Related: Singly Linked List
In the search function a value is passed as an argument and its node is returned if found, otherwise a message says “No such element in the list” and nullptr is returned.
The function starts searching from the head to the last node and passed value is matched with every node’s data item.
Here is the code for iterative search.
struct Node *search(T n)
{ //returns node of the given value
Node *node = head;
while(node != nullptr)
{
if(node->data == n)
return node;
node = node->next;
}
std::cerr << "No such element in the list \n";
return nullptr;
}
We can insert a node at front or at back of the linked list. When we insert a node at front the next node pointer points to the head of the list and then the node is made new head of the list. The value to be inserted is passed as an argument and a new node is created containing the value.
void insertFront(T val)
{
Node *node = new Node(val);
Node *tmp = head;
if (head == nullptr)
{
head = node;
tail = node;
}
else
{
node->next = head;
head = node;
node->next->prev = node;
}
}
When we insert a node at the back of the list, node is added after the tail and then the node becomes tail of the list.
void insertBack(T val)
{
Node *node = new Node(val);
if(tail->next == nullptr)
{
tail->next = node;
tail = node;
}
}
In deleteNode function the value is entered which is to be deleted. The function search the node containing the value using search function and then the node is deleted.
If the searched node is head then node next to head is made head and then the searched node is deleted. The node is deleted only if the value exists means if (node != nullptr).
void deleteVal(T val)
{
Node* find = findVal(val);
Node *tmp = head;
if(tmp == find)
{
head = tmp->next;
}
else
{
while(find != nullptr)
{
if(tmp->next == find)
{
tmp->next = find->next;
find->next->prev = tmp;
delete find;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
}
#include <iostream>
template<class T>
class DoublyLinkedList
{
struct Node
{
T data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
Node(T val): data(val), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}
};
Node *head, *tail;
public:
DoublyLinkedList(): head(nullptr), tail(nullptr) {}
~DoublyLinkedList()
{
Node *tmp = nullptr;
while (head)
{
tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
head = nullptr;
}
DoublyLinkedList(const DoublyLinkedList<T> & dll) = delete;
DoublyLinkedList& operator=(DoublyLinkedList const&) = delete;
void insertFront(T val)
{
Node *node = new Node(val);
Node *tmp = head;
if (head == nullptr)
{
head = node;
tail = node;
}
else
{
node->next = head;
head = node;
node->next->prev = node;
}
}
void insertBack(T val)
{
Node *node = new Node(val);
if(tail->next == nullptr)
{
tail->next = node;
tail = node;
}
}
void deleteVal(T val)
{
Node* find = findVal(val);
Node *tmp = head;
if(tmp == find)
{
head = tmp->next;
}
else
{
while(find != nullptr)
{
if(tmp->next == find)
{
tmp->next = find->next;
find->next->prev = tmp;
delete find;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
}
template <class U>
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const DoublyLinkedList<U> & dll){
dll.display(os);
return os;
}
private:
Node *findVal(T n) //returns node of the given number
{
Node *node = head;
while(node != nullptr)
{
if(node->data == n)
return node;
node = node->next;
}
std::cerr << "No such element in the list \n";
return nullptr;
}
void display(std::ostream& out = std::cout) const
{
Node *node = head;
while(node != nullptr)
{
out << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
};
int main(){
DoublyLinkedList<int> l1;
l1.insertFront(3);
l1.insertBack(5);
l1.insertBack(12);
l1.insertFront(6);
l1.insertBack(88);
std::cout<<l1<<"\n";
l1.deleteVal(11);
std::cout<<l1<<"\n";
return 0;
}
Reference: Introduction to Algorithms The Algorithm Design Manual Data Structures and Algorithms Made Easy