Deploying a Python Telegram Bot on Oracle Cloud
Deploying a Telegram bot on Oracle Cloud provides reliable uptime and cost-effective hosting for a wide range of bot functionalities. Here’s a step-by-step guide on setting up and deploying a bot on an Ubuntu instance in Oracle Cloud. For this example, I’ll use the Atmanam Viddhi Bot, a bot that responds to the /wisdom command, sharing random quotes from a collection on GitHub and featuring user cooldowns and interactive buttons.
Step 1: Set Up Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
-
Create a Compute Instance
-
In the Oracle Cloud Console, go to
Instances, clickCreate Instance, and follow the prompts to set up your new instance. -
Select Ubuntu 20.04 minimal as the operating system. Once created, Oracle provides an SSH key pair for secure access.
-
Save the private SSH key provided by Oracle on your local machine
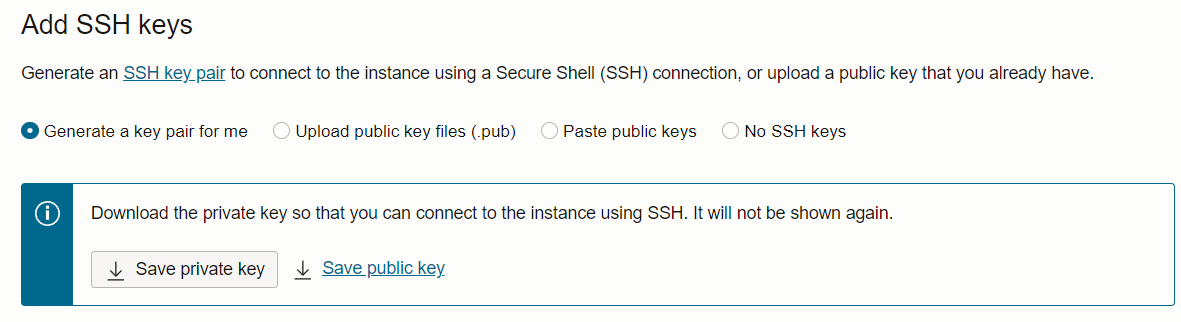
-
Ensure it has appropriate permissions by running this command:
chmod 600 path/to/downloaded/ssh-key -
-
Connect to Your Instance
- Open a terminal and connect to your Oracle instance using the SSH key saved from the setup:
ssh -i path/to/downloaded/ssh-key ubuntu@your-instance-ip - You can get
usernameandinstance-ipfrom the Oracle Cloud Console.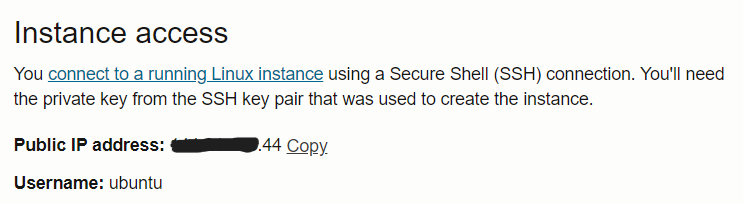
- Open a terminal and connect to your Oracle instance using the SSH key saved from the setup:
Step 2: Install Required Tools
Once connected to your instance, update your package manager and install essential tools like Python, Git, and Nano.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-pip git nano -y
Step 3: Clone Your Bot’s Repository
Next, clone the GitHub repository where the bot’s code is stored and navigate into the project directory:
git clone <repo-url>
cd atmanam_viddhi_bot
Step 4: Install Dependencies
The bot’s dependencies are managed in a requirements.txt file. Use pip to install them:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Step 5: Add Your Bot Token
Edit the .env file to securely store your bot token, which Telegram provides when you create your bot.
nano .env
In this file, add the following line with your bot’s unique token:
BOT_TOKEN=your-bot-token-here
Step 6: Configure Systemd for Bot Service
To ensure the bot runs continuously and restarts automatically if it crashes, create a Systemd service. This setup also allows you to start, stop, and monitor the bot as a service.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/atmanam-viddhi-bot.service
In this file, add the following configuration:
[Unit]
Description=Atmanam Viddhi Telegram Bot
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=ubuntu
WorkingDirectory=/home/ubuntu/atmanam_viddhi_bot
Environment=PATH=/home/ubuntu/.local/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 -u /home/ubuntu/atmanam_viddhi_bot/bot.py
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Step 7: Enable and Start the Bot Service
To apply the Systemd changes, reload the daemon, enable the service, and start it:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable atmanam-viddhi-bot
sudo systemctl start atmanam-viddhi-bot
Key Features of the Bot
The Atmanam Viddhi Bot performs a few essential functions:
- Responds to the /wisdom Command: The bot listens for a
/wisdomcommand and, when triggered, fetches a random excerpt from a GitHub repository. - User Cooldown Periods: Each user has a cooldown period between requests to prevent spam.
- Interactive Buttons: The bot sends interactive buttons, including Amazon links for relevant books, enhancing the user experience.
- Support for Multiple Simultaneous Users: The bot can handle requests from multiple users at once without interruption.
Advantages of Oracle Cloud Deployment
By deploying on Oracle Cloud, you enjoy:
- 24/7 Uptime: The bot remains active without relying on local machines.
- Automatic Crash Recovery: Systemd ensures the bot restarts if it encounters an issue.
- Easy Updates: Deploying updates to the bot is as simple as a
git pullin the project directory. - Free and Lightweight Hosting: Oracle Cloud’s free tier is ideal for bots with minimal resource requirements.
Conclusion
Deploying a Python bot on Oracle Cloud is a streamlined process, particularly with Oracle’s free tier and the support for continuous service through Systemd. With this setup, you’re able to run the Atmanam Viddhi Bot, allowing it to share wisdom with users around the clock.