Dungeons and Maps - CodinGame | C++ Implementation
The problem is from CodinGame with difficulty level Easy.
You are given N maps for a dungeon. Each map may contain a path to a treasure T, from starting position [ startRow; startCol ]. Determine the index of the map which holds the shortest path from the starting position to T, but be careful a map may lead you to a TRAP.
A path is marked on the map with ^, v, <, > symbols, each corresponding to UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT directions respectively, i.e. each symbol shows you the next cell to move on.
A valid path must start from [ startRow; startCol ] and end on T.
The path length is the count of direction symbols plus 1, for the T cell.
Read full problem here : Dungeons and Maps
We have different maps and we have to find the which map has the shortest distance to the treasure. In output we will print the index of that map.
Characters can be:
. - Empty square
# - Wall
^ - Move UP
v - Move DOWN
< - Move LEFT
> - Move RIGHT
T - The treasure square
When we encounter wall or an empty square, we cannot proceed further. Means the treasure cannot be found in that map.
We will store all maps in a vector. Each row in a map is a string and each map is a vector of strings. Width w and height h of the maps is given. So the vector to store maps is :
std::vector< std::vector<std::string> > maps(n, std::vector<std::string>(h));
Here n is the number of maps.
The integer variables start_row and start_col denote starting position on the map.
This is how vector maps will look like -
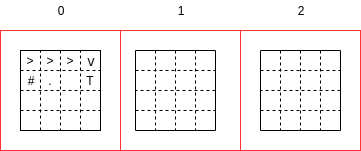
A for loop will be used to traverse through 2D verctor maps and while loop to traverse through each map.
An integer variable shortest_distance will be initialised with the highest value an integer can store.
int shortest_distance = std::numeric_limits<int>::max();
An integer variable count, stores the distance from starting position to the treasure for each map. It is initialised with 0, when processing of a map is completed and if the value of count is less than value of shortest_distance, then shortest_distance is updated with the value of count. Means we have a new map whose distance to treasure is the shortest.
For eg., after processing map at index 0, the value of count we get is 5 which is less than the value of shortest_distance. So the new value of shortest_distance is 5.
This updating of shortest_distance with new value of count is done at the end. Before that we have to terminate unnecessary processing.
For eg., while processing map at index 1, the current value of count is greater than shortest_distance(=5). So there is no need to process it anymore. It will not give us desired result even if we find treasure in the map. So, we will terminate the processing using break statement.
if (count >= shortest_distance) //current map does not have shortest distance, so break
{
break;
}
While moving up and down, the value of row is changed and while moving left and right, the value of column is changed.
So, before processing a map, integer variable next_row is initialised with start_row and next_col is initialised with start_col.
int next_row = start_row;
int next_col = start_col;
This is how we will move through the map -
if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '^') // Up
{
next_row = next_row - 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == 'v') // Down
{
next_row = next_row + 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '<') // Left
{
next_col = next_col - 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '>') // Right
{
next_col = next_col + 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '.' || maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '#') // empty sqaure or wall
{
break;
}
We will terminate the processing of the map if empty square or wall is encountered.
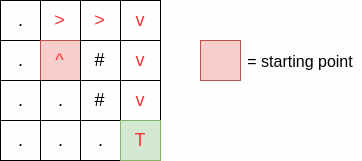
Successfully reaching the treasure -
We will have to terminate the processing if a loop in formed in a map.
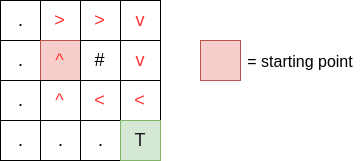
If the value of next_row is less than 0 and greater than and equal to the width of map, then we have to terminate the processing. Similarly, if the value of next_col is less than 0 and greater than and equal to height of the map, then also we have to terminate the processing.
if (next_row == start_row && next_col == start_col) //forms loop, so break
{
break;
}
else if (next_row < 0 || next_row >= width) //exceeding boundary(width)
{
break;
}
else if (next_col < 0 || next_col >= height) //exceeding boundary(height)
{
break;
}
If we found the map with shortest distance to treasure then its index number is updated to an integer variable index. Initially index was initialised with -1.
if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == 'T')//finds treasure
{
count++;
if (shortest_distance > count)
{
index = i;
shortest_distance = count;
}
break;
}
We will stop the processing once we find the treasure.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <limits>
int shortest_path_map_index(std::vector< std::vector<std::string> >& maps, int start_row, int start_col,
int num_maps, int width, int height)
{
int index = -1;
int shortest_distance = std::numeric_limits<int>::max();
for (int i = 0; i < num_maps; ++i)
{
int count = 0;
int next_row = start_row;
int next_col = start_col;
while(1)
{
if (count >= shortest_distance) //current map does not have shortest distance, so break
{
break;
}
if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '^') // Up
{
next_row = next_row - 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == 'v') // Down
{
next_row = next_row + 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '<') // Left
{
next_col = next_col - 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '>') // Right
{
next_col = next_col + 1;
count++;
}
else if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '.' || maps[i][next_row][next_col] == '#') // empty sqaure or wall
{
break;
}
if (next_row == start_row && next_col == start_col)//forms loop, so break
{
break;
}
else if (next_row < 0 || next_row >= width)//exceeding boundary(width)
{
break;
}
else if (next_col < 0 || next_col >= height)//exceeding boundary(height)
{
break;
}
if (maps[i][next_row][next_col] == 'T')//finds treasure
{
count++;
if (shortest_distance > count)
{
index = i;
shortest_distance = count;
}
break;
}
}
}
return index;
}
int main()
{
int w;
int h;
std::cin >> w >> h; std::cin.ignore();
int start_row;
int start_col;
std::cin >> start_row >> start_col; std::cin.ignore();
int n;
std::cin >> n; std::cin.ignore();
std::vector< std::vector<std::string> > maps(n, std::vector<std::string>(h));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
std::vector<std::string> map(h);
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
{
std::string map_row;
std::getline(std::cin, map_row);
map[j] = map_row;
}
maps[i] = map;
}
int map_index = shortest_path_map_index(maps, start_row, start_col, n, w, h);
if (map_index == -1)
{
std::cout << "TRAP\n";
}
else
{
std::cout << map_index << "\n";
}
}
View this on Github
If you have another solution then please share it in the comments below.