Exploring JSONB in PostgreSQL: A Beginner's Guide to Storing and Querying Structured Data
Introduction
In the realm of databases, PostgreSQL stands tall, renowned for its robust features and adaptability. Among its many offerings, JSONB shines as a versatile data type, facilitating the efficient storage and retrieval of semi-structured data. This article delves into the depths of JSONB within PostgreSQL, elucidating the process of storing and querying structured data with vivid examples.
Unraveling JSONB
JSONB, the binary manifestation of JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) data, serves as a pivotal component within PostgreSQL. JSON, a nimble data interchange format ubiquitous in web applications, finds its enhanced form in JSONB, affording a supple means to house semi-structured data within a relational database.
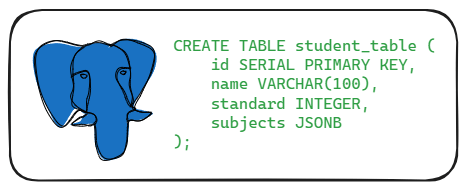
Crafting a Table with JSONB Column
Our journey commences with the creation of a modest table tailored to accommodate student data, encompassing their identities, academic standings, and an array of subjects paired with corresponding marks. Harnessing the prowess of JSONB, we ensure the fluid storage of data.
CREATE TABLE student_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
standard INTEGER,
subjects JSONB
);
Injecting Data
With our table in place, we proceed to infuse it with vitality, employing INSERT statements to populate each row with intricate details concerning the students. The JSONB column graciously accommodates the array of subjects and their respective marks.
INSERT INTO student_table (name, standard, subjects) VALUES
('John Doe', 10, '[{"subject": "Math", "marks": 90}, {"subject": "Science", "marks": 85}]'),
('Alice Smith', 11, '[{"subject": "Math", "marks": 95}, {"subject": "Science", "marks": 88}]'),
('Bob Johnson', 9, '[{"subject": "History", "marks": 85}, {"subject": "Geography", "marks": 82}]'),
('Emily Brown', 12, '[{"subject": "English", "marks": 92}, {"subject": "Physics", "marks": 87}]'),
('Michael Davis', 10, '[{"subject": "Chemistry", "marks": 88}, {"subject": "Biology", "marks": 90}]');
Querying JSONB Data
Armed with data, we embark on a quest to unearth insights, utilizing SQL queries to extract meaningful information.
- Retrieve all students with their subjects and marks:
SELECT name, standard, subjects FROM student_table;
- Retrieve students who scored more than 90 in any subject:
SELECT name, standard, subjects
FROM student_table
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM jsonb_array_elements(subjects) AS subject
WHERE (subject->>'marks')::int > 90
);
- Retrieve subjects and marks for a specific student (e.g., Alice Smith):
SELECT (subject->>'subject') AS subject, (subject->>'marks') AS marks
FROM student_table,
jsonb_array_elements(subjects) AS subject
WHERE name = 'Alice Smith';
- Aggregating Marks by Subject:
SELECT subject->>'subject' AS subject_name,
SUM((subject->>'marks')::numeric) AS total_marks
FROM student_table,
jsonb_array_elements(subjects) AS subject
GROUP BY subject->>'subject';
- Calculating Average Marks:
SELECT name, standard,
ROUND((SUM((subject->>'marks')::numeric) / jsonb_array_length(subjects)), 2) AS average_marks
FROM student_table,
jsonb_array_elements(subjects) AS subject
GROUP BY name, standard, subjects;
- Retrieving Subject Count per Student:
SELECT name, standard, jsonb_array_length(subjects) AS num_subjects
FROM student_table;
Conclusion
JSONB in PostgreSQL emerges as a formidable tool, empowering users to seamlessly manage and query semi-structured data within a relational database. With JSONB columns, the database becomes a realm of possibilities, accommodating diverse data structures and facilitating intricate queries with unparalleled efficiency. Whether you’re navigating web development landscapes or grappling with intricate data structures, mastering JSONB in PostgreSQL unlocks a realm of possibilities for your database endeavors.