Interview Question: Explain Consistent Hashing
What is Consistent Hashing?
Imagine you’re distributing candy (data) among friends (servers). If a friend leaves or joins, you don’t want to reshuffle all the candy—only what’s necessary. Consistent hashing solves this problem by minimizing data movement when servers (nodes) are added or removed. It’s used by companies like Discord, Netflix, and Amazon DynamoDB to scale their systems efficiently.
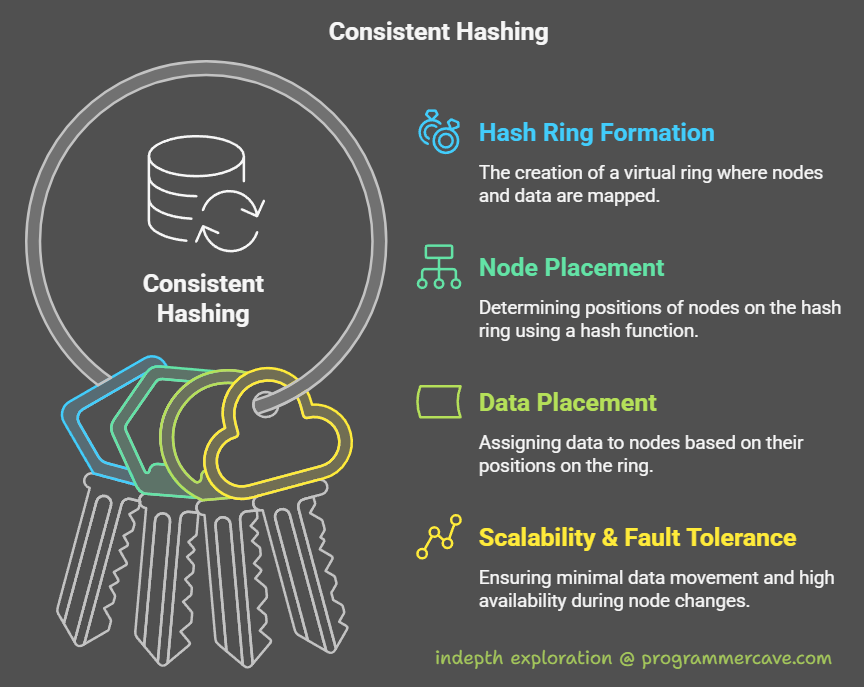
How Consistent Hashing Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. The Hash Ring: A Circular Timeline
Think of a hash ring as a clock face. Both data objects (e.g., user profiles, videos) and nodes (servers) are hashed and placed on this ring.
Example Hash Ring:
Node A (Position 10) → Data X (Position 15) → Node B (Position 20)
- Hash Function: Converts node IDs (e.g., IP addresses) and data keys (e.g., “user_123”) into positions on the ring (e.g., MD5, SHA-256).
- Placement Rule: Data is assigned to the first node found when moving clockwise on the ring.
2. Adding or Removing Nodes
- Adding a Node: Only data between the new node and the previous node is moved.
- Removing a Node: Its data moves to the next node clockwise.
Diagram:
Before: [Node A] → (Data 1, Data 2) → [Node B]
After adding Node C between A and B:
[Node A] → (Data 1) → [Node C] → (Data 2) → [Node B]
3. Virtual Nodes: Balancing the Load
To prevent one node from becoming a hotspot (handling too much data), each physical node is assigned multiple virtual nodes on the ring.
Physical Node A → Virtual Nodes (A1, A2, A3)
Physical Node B → Virtual Nodes (B1, B2, B3)
This spreads data evenly, even if some nodes are more powerful than others.
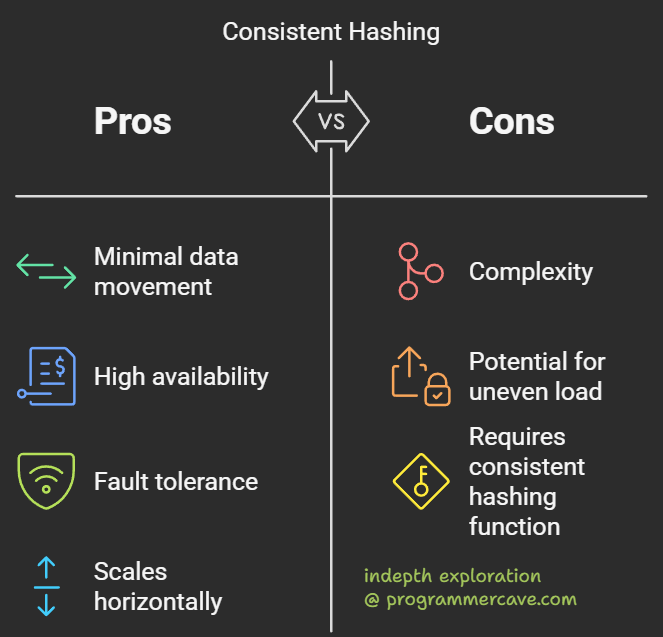
Key Benefits of Consistent Hashing
- Scalability: Add/remove nodes without reshuffling all data.
- Fault Tolerance: Failed nodes only affect their immediate data.
- Load Balancing: Virtual nodes prevent hotspots.
Challenges & Drawbacks
- Cascading Failures: If a popular data object (e.g., a viral video) is stored on one node, it might crash, shifting load to the next node and causing a chain reaction.
- Complexity: Managing virtual nodes requires more memory and logic.
Real-World Examples
- Discord: Uses consistent hashing to route messages across chat servers.
- Netflix: Distributes video content efficiently across CDN nodes.
- Amazon DynamoDB: Partitions NoSQL data dynamically.
Implementing Consistent Hashing
Data Structures
A self-balancing binary search tree (BST) is used to store node positions, enabling fast lookups (O(log n)).
Steps to Implement:
- Add a Node:
- Hash its ID and add it to the BST.
- Reassign data from neighboring nodes.
- Remove a Node:
- Delete it from the BST.
- Transfer its data to the next node.
Common Interview Questions (and How to Answer)
-
“Explain consistent hashing in simple terms.”
Compare it to a circular arrangement where data finds the next available server. Mention virtual nodes for load balancing. -
“What happens when a node fails?”
Its data is reassigned to the next node clockwise. The system remains available. -
“How do virtual nodes improve performance?”
They spread data evenly, prevent hotspots, and handle heterogeneous servers.
Final Tips for Your Interview
- Draw the Hash Ring: Visualize nodes and data placement.
- Use Analogies: Compare it to a clock or distributing candy.
- Mention Trade-offs: Discuss virtual nodes’ memory overhead.
Consistent hashing is a foundational technique for building scalable systems. By mastering it, you’ll ace system design interviews and stand out as a candidate who understands real-world distributed systems. Good luck! 🚀