Interview Question: How Does Internally Indexing Work in Databases?
Publish date: 2025-01-15
Tags:
<a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/DataBase/">DataBase</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Interview-Questions/">Interview-Questions</a>
Definition of Indexing
- Indexing is a technique used to improve the speed of data retrieval in databases by creating a separate data structure that maps search keys to their corresponding data locations.
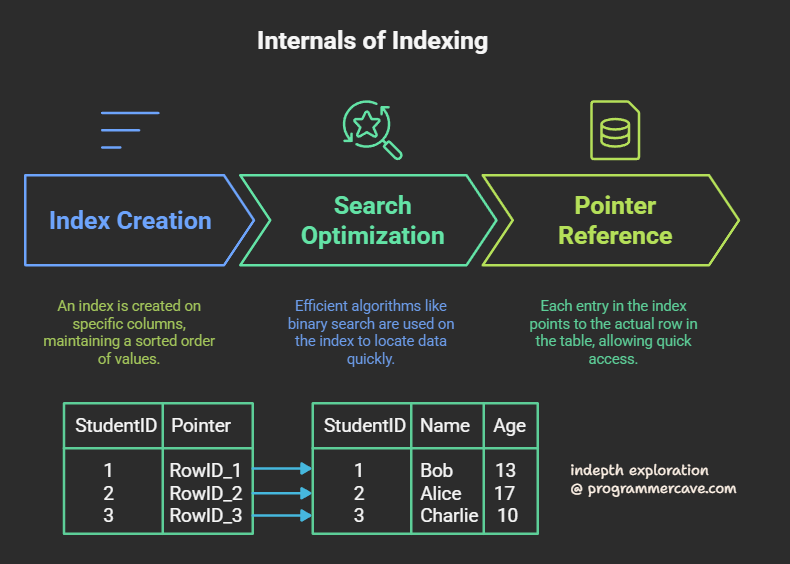
Internal Structures
-
B-Tree Structure:
- The most common structure for indexes, allowing sorted data and efficient searching, insertion, and deletion.
B-Tree Diagram
[Root] / \ / \ [A] [B] / \ / \ [C] [D] [E] [F] -
Leaf Nodes: Store actual data pointers.
-
Non-Leaf Nodes: Store keys and pointers to child nodes.
How Indexing Works
-
Data Structure Creation:
- An index is created on specific columns, maintaining a sorted order of values.
-
Search Optimization:
- Efficient algorithms like binary search are used on the index to quickly locate data.
-
Pointer References:
- Each entry in the index points to the actual row in the table, facilitating quick access.
Types of Indexes
-
Clustered Index:
- Data rows are stored in order based on the index key.
- Only one clustered index can exist per table.
- Example: Primary key often implemented as a clustered index.
-
Non-Clustered Index:
- Maintains a separate structure from data rows, containing pointers to the actual data.
- Multiple non-clustered indexes can exist on a single table.
-
Unique Index:
- Ensures that all values in the indexed column are distinct.
-
Composite Index:
- An index that covers multiple columns to optimize queries filtering by those columns.
-
Full-Text Index:
- Optimized for searching text within string columns.
Advantages of Indexing
- Improved Query Performance: Faster retrieval of rows matching specific values.
- Efficient Data Access: Reduces disk I/O operations by keeping frequently accessed data in memory.
- Optimized Sorting Operations: Avoids full table scans for sorting by using indexed columns.
- Consistent Performance: Maintains performance levels as data volume increases.
Trade-offs and Considerations
- Storage Overhead: Additional disk space is required for index structures.
- Maintenance Costs: Updates to indexed columns necessitate index updates, adding overhead during write operations.
- Choosing Right Indexes: Requires analysis of query patterns to avoid over-indexing.
Conclusion
Understanding indexing is essential for enhancing database performance by providing efficient access paths to data. Grasping its internals—such as types, structures, and benefits—enables better database design and optimization strategies.
Citations:
- Javatpoint - Indexing in DBMS
- Scaler - Indexing in DBMS
- Byjus - Indexing in DBMS Notes
- GeeksforGeeks - Indexing in Databases
- Enjoy Algorithms - Database Indexing in System Design
Tags:
<a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/DataBase/">DataBase</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Interview-Questions/">Interview-Questions</a>