Interview Question: What is Database Sharding?
Key Concepts of Database Sharding
Definition:
- Database sharding is the process of partitioning a large database into smaller, manageable pieces called shards. Each shard operates independently and contains a subset of the total data, allowing for parallel processing and improved query performance.
Purpose:
- The main objective of sharding is to effectively manage large datasets. As applications grow, a single database instance may struggle with increased data volume and user demand, resulting in slower response times. Sharding addresses these challenges by distributing data across multiple servers, enhancing both performance and scalability.
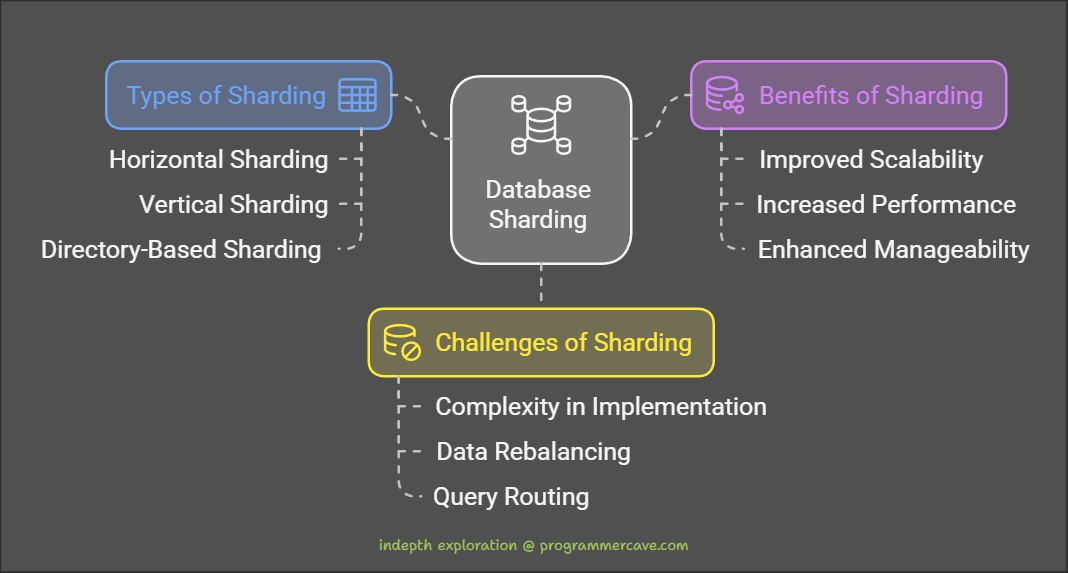
Types of Sharding:
-
Horizontal Sharding: This method divides data by rows. Each shard contains a distinct subset of rows from the original table. For instance, customer records could be split based on geographical regions.
-
Vertical Sharding: This approach partitions data by columns. Different shards contain different columns of the same table, optimizing specific queries but used less frequently than horizontal sharding.
-
Directory-Based Sharding: A central directory keeps track of which shard holds which data. This allows for dynamic management and efficient routing of queries to the appropriate shard.
Benefits of Database Sharding
-
Improved Scalability: Adding more shards enables horizontal scaling to accommodate growing datasets without significant architectural changes.
-
Increased Performance: Distributing data across multiple servers reduces the load on any single server, leading to faster query responses and better throughput.
-
Enhanced Manageability: Smaller shards are easier to manage than a single large database, simplifying maintenance tasks like backups and updates.
Challenges of Database Sharding
-
Complexity in Implementation: Designing a sharded architecture requires careful planning regarding data partitioning and shard management.
-
Data Rebalancing: As data grows or shrinks, redistributing it across shards can be complex and resource-intensive.
-
Query Routing: Efficiently directing queries to the correct shard adds overhead and complexity to application logic.
Example Scenario
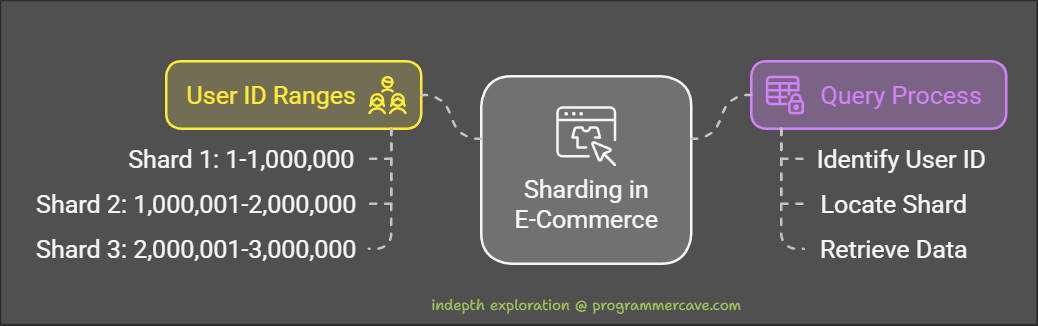
Consider an e-commerce application with millions of user accounts. Instead of storing all user records in one database, sharding could involve:
- Shard 1: User IDs 1-1,000,000
- Shard 2: User IDs 1,000,001-2,000,000
- Shard 3: User IDs 2,000,001-3,000,000
When querying user information, the system uses the user ID to determine which shard contains the relevant data, significantly speeding up retrieval times.
Conclusion
Understanding database sharding is essential for managing large-scale applications that require high availability and performance. By grasping its principles, benefits, and challenges, you can design more efficient database architectures that scale with organizational needs. Prepare well for your interviews by familiarizing yourself with this critical concept!
Citations:
- What is Sharding in DBMS?
- Data Sharding
- What is Database Sharding?
- Database Sharding: A System Design Concept
- Database Sharding Glossary
- What is Database Sharding?
- Sharding Definition
- Database Sharding Explained