Interview Question: What is the difference between SQL and NoSQL Databases?
Publish date: 2025-01-28
Tags:
<a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/DataBase/">DataBase</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Interview-Questions/">Interview-Questions</a>
SQL vs NoSQL: The Ultimate Guide for Software Engineering Interviews
Understanding the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases is a common requirement for technical interviews. Whether you’re a new grad or a seasoned engineer, interviewers often test your ability to choose the right database for specific use cases. Let’s break down these differences to help you prepare effectively.
Why SQL vs NoSQL Matters in Interviews
Interviewers assess your understanding of database fundamentals to evaluate your system design skills. Knowing when to use SQL (e.g., for financial systems) versus NoSQL (e.g., for social media apps) demonstrates your ability to balance scalability, consistency, and flexibility.
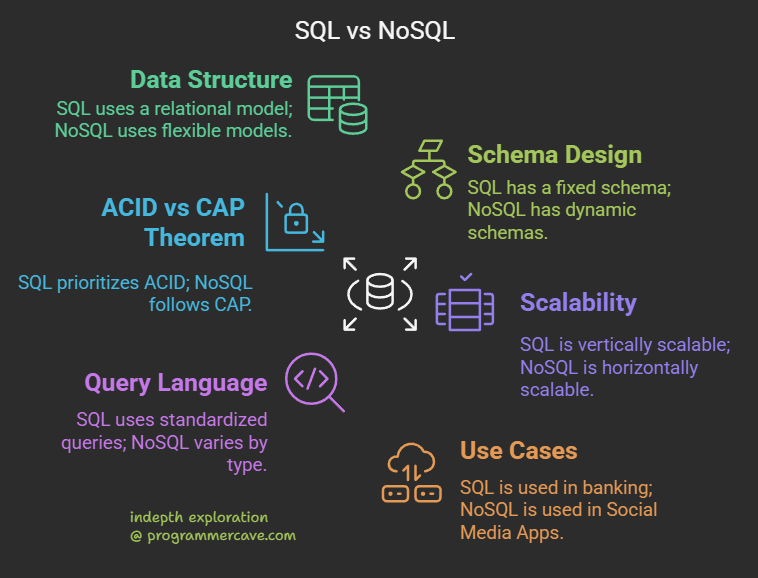
Key Differences Between SQL and NoSQL
1. Data Structure
- SQL:
Uses a rigid relational model with tables, rows, and columns. Relationships are defined via foreign keys.
Example: Customer and Orders tables linked bycustomer_id. - NoSQL:
Supports flexible models like key-value pairs (Redis), documents (MongoDB), or graphs (Neo4j).
Example: Storing JSON data without fixed schemas.
2. Schema Design
- SQL: Fixed schema requiring upfront design. Altering tables later can be time-consuming.
- NoSQL: Schema-less or dynamic schemas, ideal for evolving data (e.g., adding new fields in IoT apps).
3. ACID Compliance vs CAP Theorem
- SQL: Prioritizes ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability). Perfect for transactions needing reliability (e.g., banking).
- NoSQL: Follows CAP theorem (Consistency, Availability, Partition Tolerance). Favors availability and scalability with eventual consistency (e.g., social media feeds).
4. Scalability
- SQL: Vertical scaling (upgrading server hardware). Limited by cost and hardware constraints.
- NoSQL: Horizontal scaling (adding commodity servers). Built for distributed systems (e.g., cloud apps).
5. Query Language
- SQL: Uses standardized SQL for complex joins, aggregations, and transactions.
- NoSQL: Varies by type (e.g., MongoDB’s BSON queries, Cassandra’s CQL). Less suited for multi-table joins.
Use Cases & Examples
| Scenario | SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
| Banking/Finance | ✅ High-integrity transactions | ❌ |
| Real-Time Analytics | ❌ | ✅ Fast read/write (e.g., Cassandra) |
| Social Media Apps | ❌ | ✅ Scalability (e.g., MongoDB) |
| Enterprise CRM | ✅ Complex relationships (e.g., ERP) | ❌ |
Popular Databases:
Common Interview Questions
- “When would you choose SQL over NoSQL?”
Highlight ACID compliance, complex queries, and structured data needs. - “Explain eventual consistency in NoSQL.”
Mention CAP theorem and trade-offs (e.g., Instagram prioritizing uptime over instant consistency). - “Design a food delivery app’s database.”
Use SQL for orders/payments and NoSQL for user activity logs.
Tags:
<a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/DataBase/">DataBase</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Interview-Questions/">Interview-Questions</a>