Kangaroo HackerRank Challenge | C++ Implementation
You are choreographing a circus show with various animals. For one act, you are given two kangaroos o a number line ready to jump in the positive direction (i.e, toward positive infinity).
• The first kangaroo starts at location x1 and moves at a rate of v1 meters per jump.
• The second kangaroo starts at location x2 and moves at a rate of v2 meters per jump.
You have to figure out a way to get both kangaroos at the same location at the same time as part of the show. If it is possible, return YES, otherwise return NO.
For example, kangaroo 1 starts at x1 = 2 with a jump distance v1 = 1 and kangaroo 2 starts at x2 = 1 with a jump distance of v2 = 2. After one jump, they are both at x = 3 , (x1 + v1 = 2 + 1, x2 + v2 = 1 + 2), so our answer is YES.
Read full problem here - Kangaroo
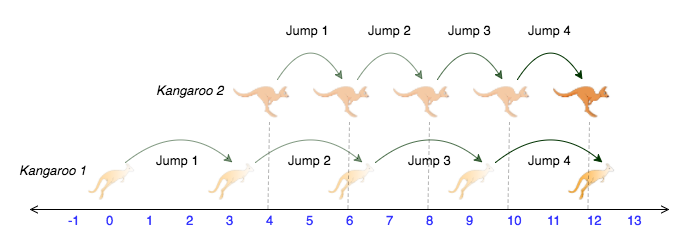
Here pos1 is current position of kangaroo 1 and pos2 is current position of kangaroo2. speed1 is speed of kangaroo 1 and speed2 is speed of kangaroo 2. difference stores the initial difference between their starting positions. The kangaroo whose position is last should cover that distance in difference number of steps because the minimum speed for a kangaroo is 1.
std::string no = "NO";
std::string yes = "YES";
int difference = abs(pos1 - pos2);
The next position for kangaroos is pos1 = pos1 + speed1 and pos2 = pos2 + speed2. If pos1 is equal to pos2 means they met and answer is YES.
Case 1: When starting positions of both kangaroo are different i.e. pos1 != pos2 and difference != 0.
Then a loop will run for difference number of times and in each step their current positions are updated and if their updated current positions are equal then return YES.
for (int i = 0; i < difference; ++i)
{
pos1 = pos1 + speed1;
pos2 = pos2 + speed2;
if (pos1 == pos2)
{
return yes;
}
}
if (pos1 != pos2)
{
return no;
}
Case 2: When starting positions of both kangaroo are same i.e. pos1 == pos2 and difference == 0.
Then next position is calculated pos1 = pos1 + speed1 and pos2 = pos2 + speed2 and if their speeds are different then new difference is calculated and proceed as case 1. If their speeds are same then they will meet in second step.
if (difference == 0 && speed1 != speed2)
{
pos1 = pos1 + speed1;
pos2 = pos2 + speed2;
difference = abs(pos1 - pos2);
}
else if (difference == 0 && speed1 == speed2)
{
return yes;
}
The kangaroos will never meet if the kangaroo whose is ahead has more speed than the last kangaroo.
if ((pos1 > pos2 && speed1 > speed2) || (pos2 > pos1 && speed2 > speed1))
{
return no;
}
Related: Roy and Code Streak HackerEarth Challenge
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <string>
std::string does_meet(int pos1, int speed1, int pos2, int speed2)
{
std::string no = "NO";
std::string yes = "YES";
int difference = abs(pos1 - pos2);
if (difference == 0 && speed1 != speed2)
{
pos1 = pos1 + speed1;
pos2 = pos2 + speed2;
difference = abs(pos1 - pos2);
}
else if (difference == 0 && speed1 == speed2)
{
return yes;
}
if ((pos1 > pos2 && speed1 > speed2) || (pos2 > pos1 && speed2 > speed1))
{
return no;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < difference; ++i)
{
pos1 = pos1 + speed1;
pos2 = pos2 + speed2;
if (pos1 == pos2)
{
return yes;
}
}
if (pos1 != pos2)
{
return no;
}
}
return no;
}
int main()
{
int x1, x2, v1, v2;
std::cin >> x1 >> v1 >> x2 >> v2;
std::string result = does_meet(x1, v1, x2, v2);
std::cout << result << "\n";
}
View this code on Github.