Efficiently Find Prime Numbers Till N: Basic vs. Sieve of Eratosthenes
Table of Content
Introduction
Are you looking for a way to find all the prime numbers till N? If so, then you have landed on the right page! In this blog post, we will discuss how to find all prime numbers till N using an optimized algorithm.
Finding all prime numbers till N is a common problem in computer science and mathematics. There are various ways to solve this problem, but we will be discussing an optimized algorithm that is efficient and easy to implement.
In our previous post we discussed different methods to check if a number is a prime number or not. - Optimized Algorithm for Checking Prime Numbers: A Comprehensive Guide
Basic Algorithm
The basic algorithm for finding all prime numbers till N is straightforward. For every number between 1 and N, we check whether it is a prime number or not. If it is a prime number, we add it to the list of prime numbers.
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(N^2), which is not efficient for large values of N. Hence, we need an optimized algorithm to solve this problem.
Optimized Algorithm
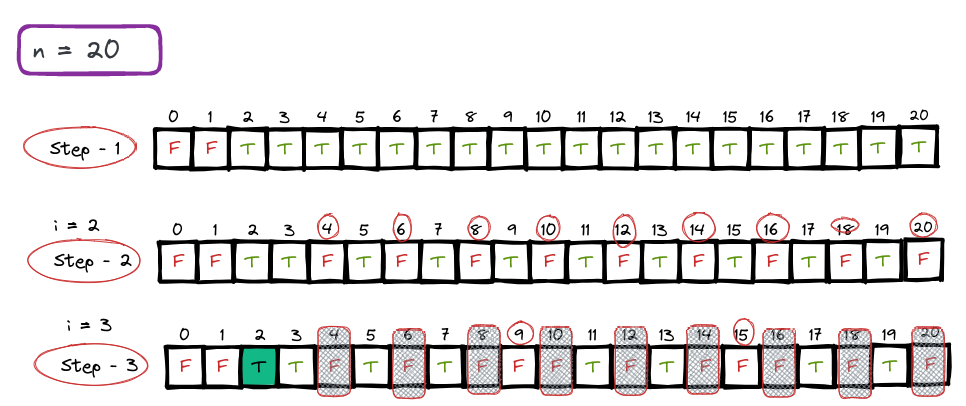
The optimized algorithm for finding all prime numbers till N is based on the Sieve of Eratosthenes. The Sieve of Eratosthenes is an ancient algorithm used to find all prime numbers up to a given limit.
The algorithm works as follows:
-
We start by assuming that every number is a prime number. We create a boolean array of size N+1, and the value at every index is set to true.
-
We start with the number 2, which is the smallest prime number. We mark every number that is divisible by 2 as a non-prime number.
-
We move to the next unmarked number, which is 3. Since 3 is still marked as true, we mark every number that is divisible by 3 as a non-prime number.
-
We continue this process until we reach the end of the array. Every number that is still marked as true is a prime number.
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(N*log(log(N))), which is much more efficient than the basic algorithm.
Implementation
Let’s implement this algorithm in C++.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
std::vector<bool> sieve(int n)
{
std::vector<bool> primes(n+1, true);
primes[0] = primes[1] = false;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
{
if (primes[i])
{
for (int j = i*2; j <= n; j += i)
{
primes[j] = false;
}
}
}
return primes;
}
The above code initializes every number as a prime number. It then starts with the number 2 and marks every number that is divisible by 2 as a non-prime number. It then moves to the next unmarked number, which is 3, and marks every number that is divisible by 3 as a non-prime number. The process continues until we reach the end of the array.
If you’d like to see the complete code for finding prime numbers till N, you can find it on my Github repository here.
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding all prime numbers till N is a common problem in computer science and mathematics. The optimized algorithm based on the Sieve of Eratosthenes is an efficient way to solve this problem. The time complexity of this algorithm is O(N log log N), which is much more efficient than the basic algorithm. We hope this blog post has helped you understand how to find all prime numbers till N.
If you’re interested in checking out some of my code related to algorithms and data structures, be sure to visit Algo-Data-Structure on Github. For my solutions to problems from competitive programming sites, you can find them in Competitive-Programming.
By the way, if you’re a teacher or parent looking for resources to help your child get ready for school, you might be interested in these fun and informative workbooks developed by a pre-school teacher. Covering all the basic skills needed for school-readiness, they’re perfect for the pre-school education niche. Check them out here: WORKSHEETS FOR PRESCHOOL