Quicksort | C++ Implementation
Like mergesort, quicksort also follows divide-and-conquer approach. The algorithm selects an element as pivot. The input array is divided into two subarrays. All elements in left subarray are less than pivot and all elements in right subarray are greater than pivot. These two subarrays are sorted independently and then merged to form a single sorted array.
Related : Merge Sort
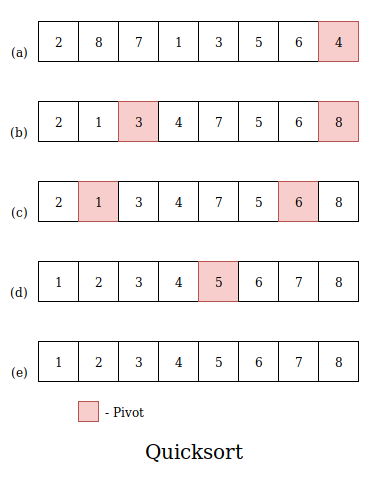
In fig. (a) 4 is selected as the pivot and in fig. (b) all elements left to the 4 are smaller than it and all elements right to the 4 are greater than it and then these two subarrays are solved independently.
The pivot element 4 in fig. (b) ends up in the correct position in the array and so on all pivot elements ends up in the correct position.
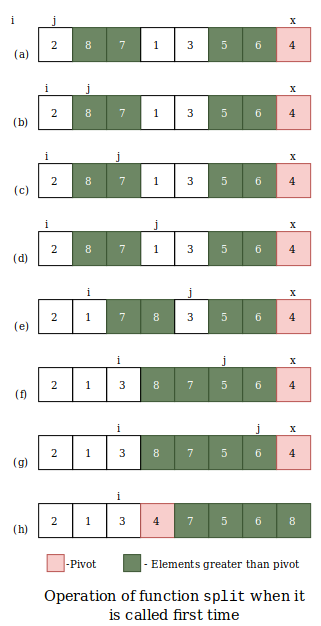
split function returns the index of pivot element.
int split(int a[], int start_index, int end_index)
{
int x = a[end_index];
int i = start_index - 1;
for (int j = start_index; j < end_index; j++)
{
if (a[j] <= x)
{
i++;
std::swap(a[i], a[j]);//swap(a[i],a[j])
}
}
std::swap(a[i+1], a[end_index]);//swap(a[i+1],a[end_index])
return i+1;
}
Here is the operation of split for the first time.
void quicksort(int a[], int start_index, int end_index)
{
if (start_index < end_index)
{
int mid_index = split(a, start_index, end_index);
quicksort(a, start_index, mid_index - 1);
quicksort(a, mid_index + 1, end_index);
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int split(int a[], int start_index, int end_index)
{
int x = a[end_index];
int i = start_index - 1;
for (int j = start_index; j < end_index; j++)
{
if (a[j] <= x)
{
i++;
std::swap(a[i], a[j]);//swap(a[i],a[j])
}
}
std::swap(a[i+1], a[end_index]);//swap(a[i+1],a[end_index])
return i+1;
}
void quicksort(int a[], int start_index, int end_index)
{
if (start_index < end_index)
{
int mid_index = split(a, start_index, end_index);
quicksort(a, start_index, mid_index - 1);
quicksort(a, mid_index + 1, end_index);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[8] = {2, 8, 7, 1, 3, 5, 6, 4};
quicksort(arr, 0, 7);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
std::cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
Reference: Introduction to Algorithms The Algorithm Design Manual Data Structures and Algorithms Made Easy Competitive Programmer’s Handbook - Antti Laaksonen
Selection sort Insertion Sort Heapsort