How to Reverse a Linked List | C++ Implementation
Publish date: 2018-01-23
Tags:
<a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Cpp/">Cpp</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Algorithm/">Algorithm</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Linked-List/">Linked-List</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Data-Structure/">Data-Structure</a>
Given a singly linked list, we have to reverse it.
Input list: { a, b, c, d, e }
Output list: { e, d, c, b, a }
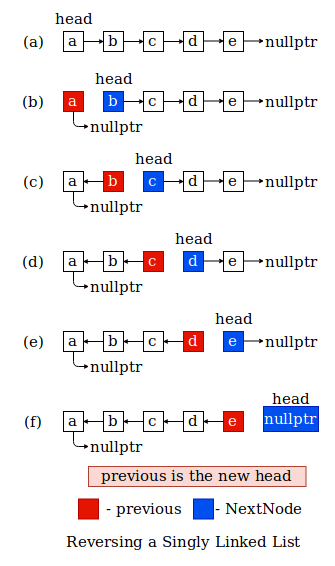
There are two ways to reverse a linked list, iterative method and recursive method.
Node* iterativeReverse(Node* head)
{
Node *previous = nullptr;
Node *nextNode = nullptr;
while(head)
{
nextNode = head->next;
head->next = previous;
previous = head;
head = nextNode;
}
return previous;
}
Node* recursiveReverse(Node* head)
{
if(head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if(head->next == nullptr)
return head;
Node *firstElement = head;
Node *secondElement = firstElement->next;
head = firstElement->next;
firstElement->next = nullptr; //unlink first node
Node *remainingList = recursiveReverse(head);
secondElement->next = firstElement;
return remainingList;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
template <class T>
class LinkedList
{
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
Node(T value) : data(std::move(value)), next(nullptr) {}
};
Node *head;
public:
LinkedList() : head(nullptr) {}
LinkedList(const LinkedList& ll) = delete; //copy constructor
LinkedList(const LinkedList&& ll) = delete; //move constructor
LinkedList& operator=(const LinkedList& ll) = delete; //copy assignment
LinkedList& operator=(const LinkedList&& ll) = delete; //move assignment
~LinkedList();
void insert(T);
void printList();
void iterativeReverse()
{
head = iterativeReverse(head);
}
private:
Node* iterativeReverse(Node* head)
{
Node *previous = nullptr;
Node *nextNode = nullptr;
while(head)
{
nextNode = head->next;
head->next = previous;
previous = head;
head = nextNode;
}
return previous;
}
};
template <class T>
void LinkedList<T>::insert(T data)
{
Node *node = new Node(std::move(data));
Node *tmp = head;
if(tmp == nullptr)
{
head = node;
}
else
{
while(tmp->next != nullptr)
{
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp->next = node;
}
}
template <class T>
void LinkedList<T>::printList()
{
Node *node = head;
while(node)
{
std::cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
std::cout<<"\n";
}
template <class T>
LinkedList<T>::~LinkedList()
{
Node *tmp = nullptr;
while(head)
{
tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
head = nullptr;
}
int main()
{
LinkedList<char> ll1;
ll1.insert('p');
ll1.insert('r');
ll1.insert('o');
ll1.insert('g');
ll1.insert('r');
ll1.insert('a');
ll1.insert('m');
ll1.printList();
ll1.iterativeReverse();
ll1.printList();
}
Reference: Introduction to Algorithms The Algorithm Design Manual Data Structures and Algorithms Made Easy
You may also like: Move all Odd numbers after Even numbers in Singly Linked List Merge two sorted Linked List (in-place) Split Singly Circular Linked List Doubly Circular Linked List Finding Length of Loop in Linked List Doubly Linked List Singly Linked List
Tags:
<a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Cpp/">Cpp</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Algorithm/">Algorithm</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Linked-List/">Linked-List</a>, <a href="https://programmercave.com/tags/Data-Structure/">Data-Structure</a>