Pointers in C++
A pointer is a special type of variable which holds the address of a value. A pointer is declared using * (asterisk).
int a = 5; //an integer variable
int * ptr; // an integer pointer or a pointer to an int
ptr = &a; // assign address of a to ptr
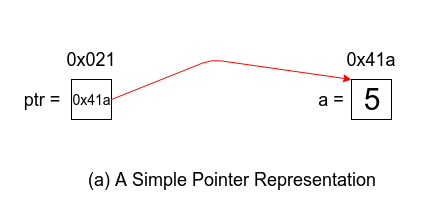
In the above figure (a), a and ptr are name of location in the memory and value stored at a is 5 and value stored at ptr is 0x41a. The address of a is 0x41a and address of ptr is 0x021. So ptr stores the address of a and we can also define another pointer which stores the address of ptr i.e. 0x021.
ptr will output value stored in it and *ptr will output the value stored at address stored in ptr.
std::cout << ptr << "\n"; // 0x41a
std::cout << *ptr << "\n"; // 5
std::cout << &a << "\n"; //0x41a
Since ptr is pointing at a, value stored in a can be modified by *ptr.
*ptr = 10;
std::cout << *ptr << "\n"; // 10
std::cout << a << "\n"; // 10
Similarly, a pointer to char or a pointer to double is declared.
A constant pointer only points to the object it was initialized to. If it was initialized to point to an integer variable a, then it cannot be changed to point to another integer variable b. This means that the address stored in a constant pointer cannot be changed.
int a = 5;
int * const ptr = &a; // a constant pointer
A constant pointer must be initialized when it is declared. The following lines of code will produce an error.
int * const ptr; // Error
ptr = &b //Error
The value stored in a can be changed. It can be changed by modifying a or by modifying *ptr.
a = a + 5;
std::cout << a << "\n"; // 10
*ptr = *ptr + 5;
std::cout << *ptr << "\n"; // 15
In a pointer to a constant, the pointer can not be used to modify the value at which it points.
int a = 5;
const int * ptr = &a;
a = a + 5;
std::cout << a << "\n"; // 10
*ptr = *ptr + 5; // Error
When 1 is added to an integer variable, the value stores in it increases by 1. Similarly when a pointer is incremented by 1 it points to next address.
If it is a pointer to an int, then its the value in it is increased by 4 bytes and if it is a pointer to a char, then the value in it is increased by 1 byte.
int arr[] = {1, 3, 5};
int * ptr = &arr[0];
std::cout << *ptr << "\n"; // 1
ptr++;
std::cout << *ptr << "\n"; // 3
ptr++;
std::cout << *ptr << "\n"; // 5
Watch Pointers in C++ explanation in Hindi on Youtube.
Practice the programs to have a good grasp on Pointers.
Move all Odd numbers after Even numbers in Singly Linked List Merge two sorted Linked List (in-place) Split Singly Circular Linked List Reverse the Linked List Finding Length of Loop in Linked List